Nitrogen gas is a crucial component for various industrial applications. With its inert, stable, and non-flammable properties, nitrogen acts as a reliable blanket gas and atmosphere control in processes where oxygen contamination poses a risk. From food freezing and packaging to electronics manufacturing and pharmaceutical production, industries rely on a consistent supply of high-purity nitrogen.
Rather than relying on delivered tanks or liquid nitrogen, many companies are switching to on-site nitrogen generation for greater supply flexibility, cost savings, and independence. On-site nitrogen generators produce nitrogen gas from standard compressed air, eliminating the need for external supply.
Of the main generator technologies, PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) nitrogen generators are the preferred choice when high flow rates and purity levels are required. This article takes an in-depth look at how PSA nitrogen generators work and their key benefits.
Overview of PSA Nitrogen Generation
PSA nitrogen generators utilize a specialized separation technique called Pressure Swing Adsorption to produce purified nitrogen gas from compressed air. This process involves pressurizing the air and passing it through one or more vessels filled with an adsorbent material, usually carbon molecular sieve (CMS).
The CMS adsorbs oxygen, argon, and other trace gases from the feed air, while allowing high-purity nitrogen to pass through. The adsorbed gases are then desorbed and purged using pressure swings that regenerate the CMS beds. This cycle is repeated continuously to provide a steady stream of nitrogen gas.
Compared to alternatives like delivered nitrogen and membrane nitrogen generators, PSA systems are unmatched in their ability to produce high purity (up to 99.999% pure) nitrogen reliably at high flow rates. This makes them well-suited to industrial applications with stringent demands.
Key Components of a PSA Nitrogen Generator
A PSA nitrogen generator contains several key components engineered to work together seamlessly:
- Air compressor – Provides feed air to the PSA system at the required pressures
- Air treatment system – Removes moisture, particulates, and hydrocarbons from the feed air to prevent contamination
- Molecular sieve beds – Twin towers filled with CMS adsorbent to separate the nitrogen
- Nitrogen receiver – Stores the separated high-purity nitrogen temporarily
- PLC control panel – Automates the PSA cycle through timers and solenoid valves
- Piping, valves, and instruments – Connect the components and control the process
The PSA process itself occurs inside the molecular sieve beds, which are filled with CMS adsorbent. The adsorbent’s properties and the PSA cycle timing allows the nitrogen separation to occur consistently.
How Does the PSA Cycle Work?
The PSA cycle involves coordinated pressure swings in the adsorbent beds to selectively adsorb and desorb gases. There are four main steps:
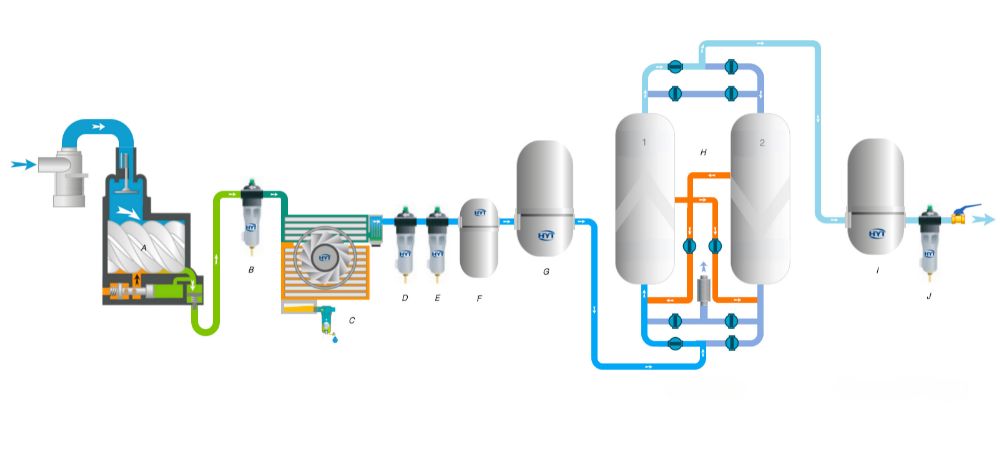
Feed Pressurization – The bed is brought online and feed air enters, increasing the pressure. Nitrogen passes through while oxygen and argon are adsorbed.
Production – The bed stays pressurized and continues producing nitrogen until the adsorbent nears saturation.
Depressurization – The bed is taken offline and pressure drops, causing adsorbed gases to desorb.
Purge – A small amount of product nitrogen purges the bed, prepping it for the next cycle.
The PSA cycle is then repeated for the other bed, allowing constant production. The timing, number of beds, and pressures dictate the purity and flow rate of the nitrogen produced.
PSA Purity Levels and Capacities
PSA nitrogen generators can produce a range of purity grades to suit different industrial applications:
- 95-97% purity for 50-5000 Nm3/hr flow
- 97-99% purity for 30-3000 Nm3/hr flow
- Up to 99.9999% ultra high purity for 10-1000 Nm3/hr
Food packaging, dairy production, and electronics manufacturing often use 99.9% pure nitrogen. Meanwhile, purities above 99.999% are essential for pharmaceuticals, laboratories, and gas industries requiring zero contamination.
Operating and Maintaining a PSA Nitrogen Generator
While PSA nitrogen generators run reliably with minimal supervision, periodic maintenance is key to longevity and performance. This involves:
- Replacing air filters and CMS beds per manufacturer schedule
- Checking/replacing valves, seals, and instrument parts
- Monitoring process parameters like pressure and flow
- Keeping feed air clean and dry to maximize CMS life
With proper care, PSA nitrogen generators can operate for years before major overhauls. Some periodic maintenance is required, but companies save tremendously compared to outsourced nitrogen supply.
The Benefits of On-Site PSA Nitrogen Generation
Installing an on-site PSA nitrogen generator offers companies major advantages over traditional delivered nitrogen options:
- Lower long-term costs – Eliminates recurring delivery fees and product markup
- Supply flexibility – Flow rate adjusts to match demand. No supply bottlenecks.
- Consistent purity – Strict quality control of product nitrogen
- Independence – Not affected by supplier price hikes or distribution problems
- Safety – No risks associated with handling high-pressure gas cylinders
With PSA technology, on-site nitrogen generation is a growing trend across industrial sectors. For a high purity nitrogen solution with maximum flexibility and cost savings, PSA nitrogen generators are an ideal choice.
If you’re interested in receiving tailored advice on implementing PSA nitrogen generation at your facility, contact Oxynitra today. Our engineers can help select the optimal generator sizing and purity grade to match your specific nitrogen needs. The sooner your business switches to on-site production, the faster the savings add up.

